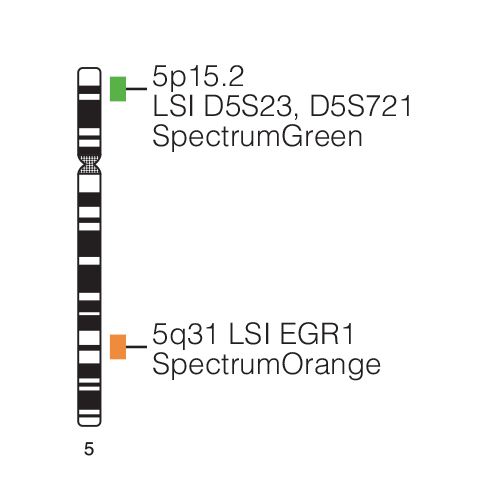
A study suggests that haplo-insufficiency of EGR1 may play a role in leukemogenesis. The Vysis locus-specific identifier (LSI) EGR1 SpectrumOrange/D5S23,D5S721 SpectrumGreen Probes, components of the Vysis EGR1FISH Probe Kit, have been used in several studies to detect EGR1 deletions. A study, conducted as part of an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) clinical trial, demonstrated the utility of the interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) technique to stratify patients into cytogenetic risk categories at diagnosis of AML using the Vysis LSI EGR1 SpectrumOrange/D5S23, D5S721 SpectrumGreenProbes in conjunction with several additional FISH probes. In addition, the prognostic importance of chromosome 5 abnormalities has been established in several large clinical studies. The prognostic clinical utility of detecting specific chromosomal abnormalities in bone marrow specimens from patients diagnosed with AML is firmly established in both standard medical practice guidelines and in the medical literature.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Practice GuidelinesTM for Acute Myeloid Leukemia, which are the consensus recommendations of leading US AML experts, state that cytogenetics is the single most important prognostic factor in AML. More specifically, the guidelines provide different risk categories for patients depending upon cytogenetic or molecular abnormalities. As an example, patients with deletion of chromosome 5q are in the ‘poor risk’ category and may have an unfavorable prognosis. The Vysis EGR1 FISH Probe Kit uses FISH DNA probe technology to determine deletion status of the probe target for LSI EGR1, and the LSI D5S23, D5S721 probe serves as a control.
The clinical utility of the cytogenetic detection of the deletion of chromosome 5q is correlated with reduced 5-year overall survival in studies by Byrd et al1 and Grimwade et al. The Byrd publication demonstrated the prognostic value in 86 patients with a -5/5q abnormality by a median overall survival (OS) of 0.3 years compared to the median OS of 1.3 years associated with patients exhibiting a normal karyotype. Patients with a -5/5q- abnormality had a 5-year OS of 6% compared to a 5-year OS of 24% associated with patients exhibitinga normal karyotype. Patients with a -5/5q- abnormality also had a significantly lower complete remission (CR) rate of 31% than the normal karyotype, which resulted in a CR of 68% with a p < 0.001. For del(5q), 42 patients had a 5-year OS of 5%, (95% CI 2 – 13%) and median overall survival of 0.3 years. Grimwade et al, showed prognostic value in 28 patients for 5q-. Cytogenetic abnormalities in the Medical Research Council (MRC) AML10 clinical trial for del(5q) patients showed 5-year OS of 11% and CR of 57% in the adverse risk group. These values varied significantly from the no abnormality, or normal karyotype group, which had 5-year OS of 42% and CR of 88% (p <0.001).
The publication “Utility of interphase FISH to stratify patients into cytogenetic risk categories at diagnosis of AML in an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) clinical trial (E1900)” by Vance et al,2 establishes linkage between cytogenetic results and the Vysis EGR1 FISH Probe Kit. When 181 bone marrow specimens were compared to cytogenetic results at the > 6% cut- off, there was overall agreement of 98.90% (179/181) (95% CI 96.06% – 99.70%), negative percent agreement of 100% (171/171) (95% CI 97.80% – 100.00%) and positive percent agreement of 80% (8/10) (95% CI 49.02% – 94.33%).
REFERENCES:
1. Byrd JC. Mrozek K, Dodge RK, et al. Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative incidence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Gorup B (CALGB 8461). Blood. 2002;100:4325-36.
2. Vance GH, Kim H, Hicks GA, et al. Utility of interphase FISH to stratify patients into cytogenetic risk categories at diagnosis of AML in an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) clinical trial (E1900). Luek Res. 2007;31:605-9.